Basic Structure of C Program
- A well-structured C program makes debugging easier
- It increases the readability and modularity of the code
- It is defined by its control flow
- Structures are built up of blocks of codes
- Blocks have a single entry and exit in the control flow
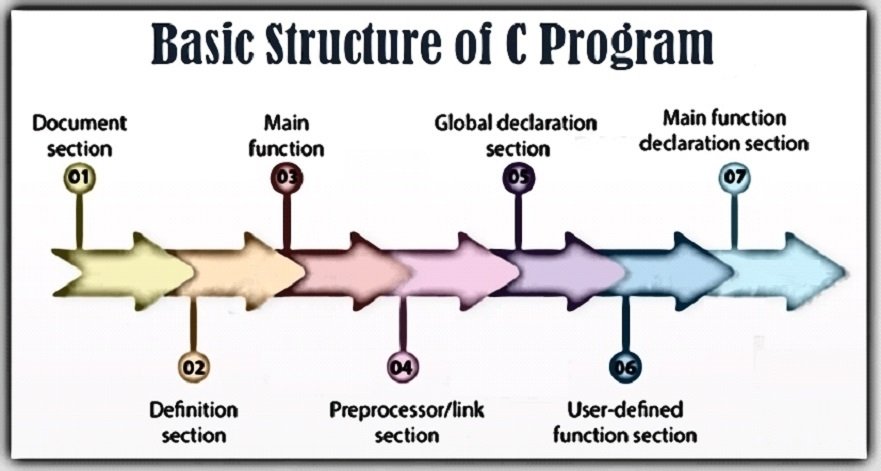
The Basic Structure of a C Program is comprehensively divided into seven parts for different purposes. It makes the program easy to read and easy to modify. These parts are-
Documentation Section: It covers the statement stated at the beginning of a program, such as a program’s name, date, description and title.
Definition Section: The Definition Section comprises of various constants declared using the define keyword.
Main Function Section: Main() is the first function to be executed by the computer. It is necessary for a code to include the main(). It is like any other function available in the C library.
Link Section: The Link Section supplies instructions to the compiler to link functions from the system library.
Global Declaration Section: The Global Section comprises of all the global declarations in the program.
User-defined Function Section: The User-defined functions specified the functions specified as per the requirements of the user.
Declaration Section: It names a type and specifies a sequence of variable values (called “members” or “fields” of the structure) that can have different types.
also read:
| HTML | DATA STRUCTURE |
| DBMS | REASONING |
| C PROGRAM | APTITUDE |
| E-LEARNING |







